How DSPA works
DSPA aerosol generators consist of a solid aerosol forming compound in a non-pressurized red canister which aerosolizes finely divided solid particles: the aerosol fire extinguishing agent. The aerosol is self-generated by a combustion process of the solid aerosol-forming compound, activated by an activation device, also known as the starter.
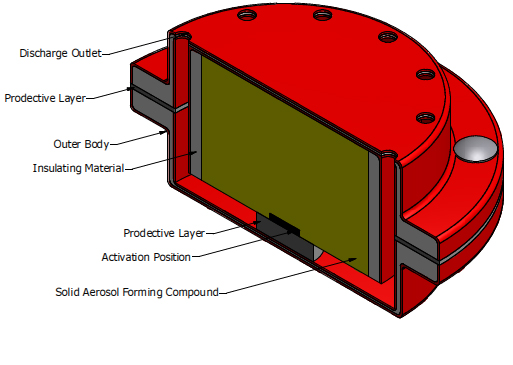
Aerosol
DSPA aerosol was originally developed as an alternative to Halon and other conventional extinguishing agents. DSPA Aerosol is uniquely safe and effective. The active substances of the DSPA aerosol are solid micro particles that fill the compartment completely and attack the combustion process of a fire at a chemical level. As a result, the flames are instantly knocked down and the energy removed from the fire.
The amount of extinguishing agent required is significantly less than that of conventional extinguishing agents like CO2, FM200, Inergen etc. Additionally DSPA aerosol offers significant installation and maintenance savings: It does not require any pressure vessels, manifolds, nozzles or pipe work. Furthermore, unlike other agents, DSPA is environmentally friendly.

Extinguishing Mechanism
Unlike many other extinguishing agents, DSPA Aerosol interferes with the chain reaction in the fire, leaving oxygen levels intact.
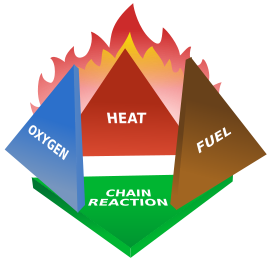
“Fire propagation” radicals (OH, H, and O) are essential elements to the chain reaction of the fire. DSPA Aerosol suppresses the fire (primarily) by chemical interference with these free radicals within the fire zone, thus interrupting the on-going chain reaction of the fire.
DSPA Aerosol is an extinguishing medium of finely divided solid particles, mainly potassium particles, with a typically diameter of approx.. 2 microns. When introduced into the flaming region of a fire, the aerosol reacts with the fire radicals produced during combustion (hydrogen, oxygen, and hydroxyls) resulting in extinguishment of the fire. The small aerosol particles provide a large surface area for capturing these radicals making them effective extinguishing agents.